
Pulmonary
ArteriovenousMalformations
Pulmonary
ArteriovenousMalformations

Pulmonary AVMsEtiology
Congenital defect in capillary structure
Acquired in
Cirrhosis
Cancer
Trauma
Surgery
Actinomycosis
Schistosomiasis

Pulmonary AVMsEtiology
Pathology
Hemangioma of cavernous type
Age
3rd–4th decade
Mostly manifest in adult life
10% in childhood

Pulmonary AVMsOccurrence
Isolated abnormality=40%

Pulmonary AVMsOsler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome
Associated with Osler-Weber-RenduSyndrome (30-88%)=hereditary hemorrhagictelangiectasia
Only 15% of Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome havepulmonary AVMs
Family history with this disease
Epistaxis common
Telangiectasia of skin and mucus membrane
GI bleeding

Multiple AVMs in Liver in Osler-Weber-RenduSyndrome
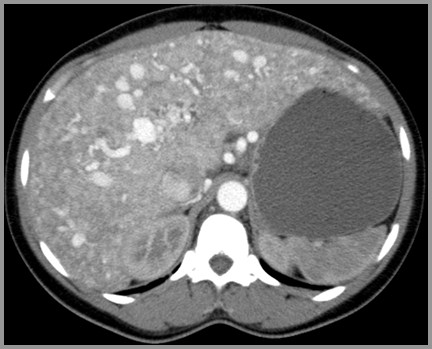

Pulmonary AVMsTypes
Simple type (79%)
Single feeding artery empties intobulbous, nonseptated aneurysmalsegment
Single draining vein

Pulmonary AVMsTypes-continued
Complex type (21%)
More than one feeding artery emptiesinto septated, aneurysmal segment
More than one draining vein

Pulmonary AVMsSymptoms
Asymptomatic in most until 3rd or 4thdecade if AVM is single and <2cm
Orthodexia = increased hypoxemia withPaO2<85 in erect position
Epistaxis (79%)
Cyanosis with normal-sized heart (R Lshunt in 25-50%)

Pulmonary AVMsSymptoms-continued
Clubbing
Bruit over the lesion which > withinspiration
Dyspnea on exertion (60%)
Palpitations, chest pain, no CHF

Pulmonary AVMsLocation
Lower lobes (65-70%)
Then, middle lobe
Then, upper lobes
Medial third of lung
Often subpleural
Bilateral (20%)
As opposed to multiple which is 33%

Pulmonary AVMsX-Ray Findings
Sharply defined mass (90%)
Cord-like bands from mass to hilum(feeding artery and draining vein)
2/3 single, 1/3 multiple
Enlarge with advancing age

Pulmonary AVMsX-Ray Findings
Change in size with Valsalva maneuver(decrease)
Phleboliths (rarely)
CT
Feeding vessels
Rapid enhancement on dynamic CT

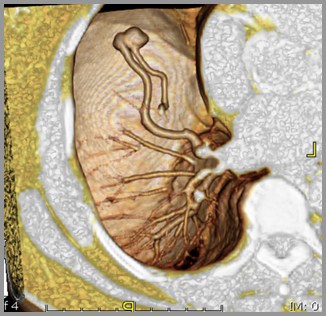
Pulmonary AVM – 3D CTReconstruction
Heart

Pulmonary AVMsComplications
CVA
TIA (37%)
Stroke (18%)
Cerebral abscess 2° to loss ofpulmonary filter function (9%)

Pulmonary AVMsComplications-Continued
Hemoptysis 2° rupture into bronchusmost common presenting symptom(13%)
Hemothorax 2° rupture of subpleuralAVM
Polycythemia

Pulmonary AVMsPrognosis
11% mortality

Pulmonary AVMsDDX
Other causes of solitary ormultiple pulmonary nodule(s)
Ca
Hamartoma, adenoma, granuloma
Mets
Wegener's
Rheumatoid nodules


Pulmonary AVMsTreatment
Embolization with coils/detachableballoons